Making a successful transition to the latest lease accounting requirements, such as ASC 842, IFRS 16 or GASB 87, is a threefold process of understanding the standards and their impact on a business and its accounting practices, identifying and gathering the necessary lease data, and implementing a lease accounting solution that will aid in achieving and maintaining compliance.
What is Lease Accounting?
Lease Accounting is the process of recording and reporting on all of the leased property, equipment, and other non-owned assets that a business or other organization holds.
Under the requirements of the latest lease accounting standards — ASC 842, IFRS 16, GASB 87, as well as local versions of each — all leases and similar contracts (not just capital leases) must now be accounted for as assets and liabilities on the balance sheet. Therefore, lease accounting requires the ability to gather accurate lease data and update the information as the terms change (when lease terms are renewed, canceled, and so on).
The use of a software solution for tracking, updating, and managing leases helps to ensure the accuracy of the data that is needed for disclosure reports, both for initial adoption and for long-term reporting.
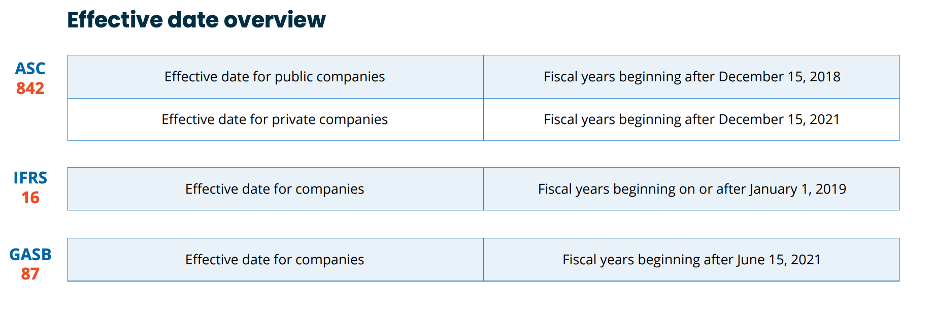
What are the New Lease Accounting Standards?
ASC 842, which replaces the lease accounting standard ASC 840. The purpose of ASC 842 is to increase disclosure and visibility into the leasing obligations of both public and private organizations. Where previously most leases were not included on the balance sheet, the ASC 842 standard requires companies to report right-of-use (ROU) assets and liabilities for almost all leases.
IFRS 16, which replaces the lease accounting standard IAS 17. IFRS 16 changes the way companies account for leases in their financial disclosures, including balance sheets and income statements. Under IFRS 16, all leases are considered finance leases.
GASB 87 was created to increase visibility into lease obligations and remove ambiguity around lease obligations in financial disclosures, particularly balance sheets and income statements.
What is Lease Accounting Software?
Lease accounting software provides tools to input and report on all the financial aspects of leases to meet the new compliance requirements. The technology performs critical accounting calculations and automates the process of adding information to the balance sheet, including ROU assets, interest expenses, liabilities, practical expedients, and other elements required under FASB and IASB guidance.
What Common Risk does Lease Accounting Software Solve?
Without a lease accounting solution to help with lease tracking, reporting, and management, your business may be exposed to a number of risks, including:
- Inconsistencies in the way assets are accounted for
- Human error in calculations or in migrating data from one source to another
- Widely dispersed lease records rather than a central data repository
- Lack of visibility into lease terms, changes, and important dates
- Missing details such as embedded leases that are part of a larger contract
- Lack of a structured change management process
- Mistakes in complex calculations for common area maintenance (CAM) and other costs
- No record of what changes have been made to leases, when, and by whom
- Increased odds of failing an audit
This is because lease documents and the standards contain many intricacies.
The new lease accounting standards are complex of necessity, to capture the challenging and dynamic nature of the underlying agreements. Therefore, reporting on assets and liabilities is extremely difficult without software.
What are Some Important Lease Accounting Software Features?
To meet compliance effective dates AND get optimal ongoing value from a lease accounting solution, you want to be sure it delivers the features and functions you need, and is as quick and easy to deploy as possible. The following are some features to look for:
- Compliance
- Reporting
- Integrations
- Centralized Accounting and Administration
- Ease of Implementation
- Ease of Use
- Security
- Future Readiness
What to do While Evaluating Lease Software?
Preparing for lease accounting compliance is a time-consuming and complex process. Therefore, even as you are evaluating software solutions and their providers, you can (and should) get a jump on preparing for compliance and the implementation of a lease accounting solution.
Who in your business should be involved in lease accounting compliance?
Naturally, the accounting team is at the core of lease accounting compliance activities. However, this team will need help from others within the business to gather all the data required for lease accounting calculations and disclosures.
In addition, people in your business who regularly work with leases can offer valuable insights into how your company’s leases function and where to find critical data. There may also be numerous departments or locations in your company that individually negotiate and manage leases.
What lease information do you need to gather?
The following tips will help in the process of identifying all the leases that your company holds and gathering the necessary lease data:
- Ask all lease stakeholders to begin conducting a lease inventory. This involves finding and reviewing all lease documents and contracts — most likely including paper records that may be tucked away in file drawers.
- Closely examine all contracts to identify embedded lease components, such as service agreements that are part of larger contracts.
- Review your company’s AP check run to identify all the vendors your company pays on a recurring basis and find any leases that may be missing from other records.
- Select practical expedients, which affect which lease details you will need to collect.
- Determine which data points you need to track for every lease to calculate lease liabilities and ROU assets, as well as to create disclosure reports.
- In addition to payment information, gather details such as commencement dates, termination clauses, and options to renew or purchase.
For compliance, you’ll also need to create:
- Policies that document how you have interpreted the lease accounting guidance
- Procedures that spell out the steps you’ll take to achieve compliance according to your policies, including how you will collect, aggregate, and migrate data into your lease accounting system
Documenting these policies and procedures will not only prepare you to address any questions from auditors or your organization’s financial officers — it will also help you maintain practices throughout your lease data collection and reporting process.
When Should You Start Collecting Lease Data?
Collecting lease data is a lengthy and complex process — one that can take some companies many months, depending on how many leases and how they are currently stored. Even for a company with a relatively small number of leases, the task is time-consuming.
Companies often underestimate the time it will take to find documents, identify embedded leases, and identify and extract lease data. Waiting too long to begin the process can result in missing the compliance effective dates – or rushing the process and publishing incomplete and inaccurate financial reports.
Therefore, it is crucial to start the data collection process as soon as possible, even before you’ve selected a lease accounting product.
What Benefits can you Anticipate Once Lease Accounting Software is in Place?
Lease accounting may have been manageable in the past using a spreadsheet or other manual method. However, the added complexity due to the new lease accounting standards, ASC 842 and IFRS 16, means there are:
- Many more data points to track and audit
- More demanding disclosure requirements
- Greater impact on financial statements
Once you have implemented a lease accounting system and populated it with your lease data, the business will benefit from:
- Improved efficiency with the ability to automatically generate calculations, journal entries, and disclosure reports
- More consistent and accurate calculations with an automated system that mirrors your accounting policies and procedures
- Improved accountability with audit trails for tracking changes and drilling down to lease data details
There are many rules and regulations associated with the new lease accounting guidelines. How do you know where to begin? To learn more about lease accounting, download this complete guide to lease accounting.




